Anything that puts enough force on your knee to bend or twist it farther than its natural limit can tear your ACL.
The ACL is one of your knee ligaments. It connects your thigh bone (femur) to your shin bone (tibia). You have one ACL in each knee. It forms an “X” shape inside your knee with your posterior cruciate ligament (PCL). The ACL is closer to the front of your knee. The PCL is closer to the back of your knee.
Your ACL is like a strap that connects your bones and prevents your knee from bending or rotating too much. Anything that puts enough force on your knee to bend or twist it farther than its natural limit can injure or tear your ACL.
ACL tears are a common injury, especially among athletes. Visit a healthcare provider if your knee hurts, particularly if the pain started after an injury or physical activity.
An ACL tear is an injury to your knee’s anterior cruciate ligament (ACL).
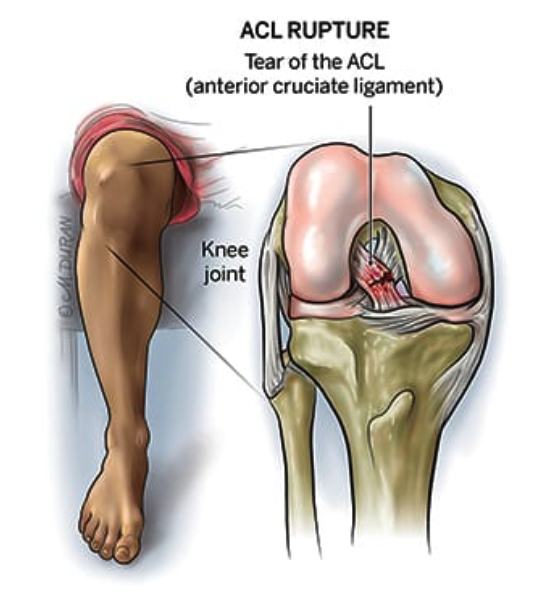
The ACL is the most commonly injured knee ligament. Sports injuries usually cause ACL tears. If you tear your ACL, you’ll probably need surgery to reconstruct it. Most people who tear their ACL make a full recovery and resume playing sports with no long-term consequences. The recovery time for a torn ACL is usually six to nine months.
ACL injuries are classified into three grades based on severity:
ACL injuries and tears are very common. The ACL is the most commonly injured knee ligament. Experts estimate that between 100,000 and 200,000 people in the U.S. tear an ACL each year.
Most people know the moment they tear their ACL. Sports injuries and other traumas that tear your ACL are usually obvious enough that you can say exactly when it happened.
People who experience an ACL tear usually feel or hear a pop in their knee. Their knee might give out (feel unstable and weak). ACL tears can be very painful, with knee swelling, but some people only feel small discomfort and instability. Visit an orthopaedic doctor if you injured your knee, especially if you hear or feel a popping.
The severity of symptoms depends on the extent of the injury. Some of the most common ACL sprain symptoms include:
Many people report hearing or feeling a loud “pop” when the ligament tears. This is often the first sign of an ACL injury.
Pain is usually felt deep inside the knee, particularly at the centre or along the joint line. It may intensify when trying to bear weight.
Swelling develops rapidly within a few hours due to internal bleeding in the knee. It may cause stiffness, limiting movement.
An injured ACL compromises knee stability, making it difficult to stand, walk, or pivot. Many individuals feel like their knees might “give out.” Difficulty in climbing stairs, specifically Climbing downstairs
Bending or fully straightening the knee becomes painful and difficult due to swelling and joint stiffness.
If left untreated, an ACL tear can lead to chronic knee instability and increase the risk of further injuries, such as cartilage damage requiring cartilage repair.
ACL injuries typically occur due to excessive strain on the ligament. ACL tears happen when your knee moves or twists more than it naturally can. The most common causes include:
Quick turns, pivots, or side-step movements can overstretch the ACL, leading to tears.
Landing awkwardly after a jump increases stress on the knee, putting the ligament at risk.
A sudden blow to the knee, such as in contact sports or car/bike accidents, can rupture the ACL.
Extending the knee beyond its normal range can strain and tear the ligament.
Weak quadriceps and hamstrings fail to support the knee, increasing susceptibility to ligament injuries.
Anyone can experience an ACL tear. They’re much more common among athletes, especially those who play sports that involve suddenly stopping, twisting or changing directions. Some sports that cause frequent ACL tears include:
The injuries that cause ACL tears can damage other parts of your knee, too.
You might damage or tear your other knee ligaments during an ACL tear, including your:
Other injuries that can occur at the same time as an ACL tear include:
A doctor will diagnose an ACL tear by performing a physical exam and some tests. They’ll ask you about your symptoms and look at your knee. Tell your doctor what you were doing right before you hurt your knee and when you first noticed symptoms.
Your doctor might perform some movements or motions with your knee and leg. These tests might feel uncomfortable. Tell your doctor if any position or motion hurts or worsens your symptoms.
You’ll probably need a few imaging tests, including:
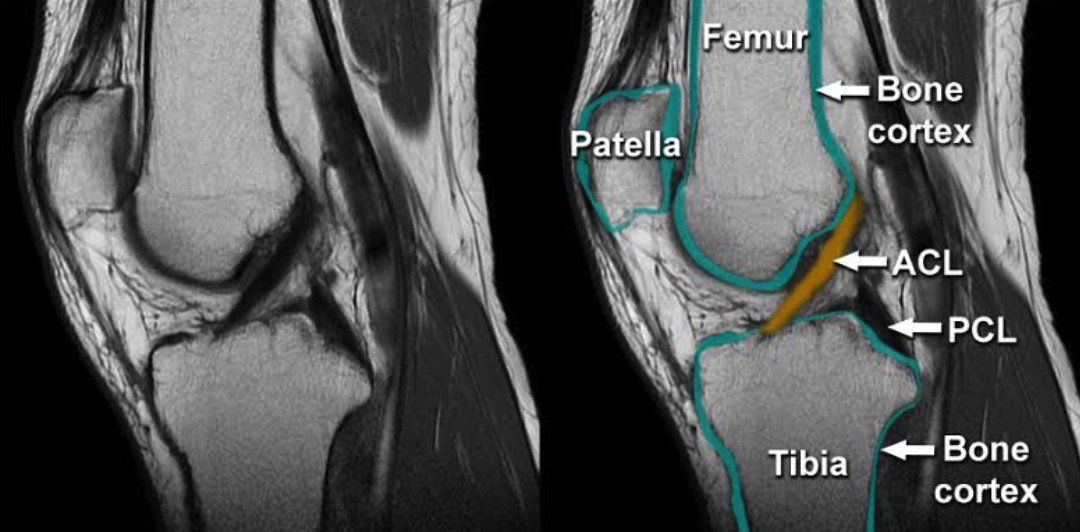
Treatment depends on the severity of the tear and the patient’s lifestyle.
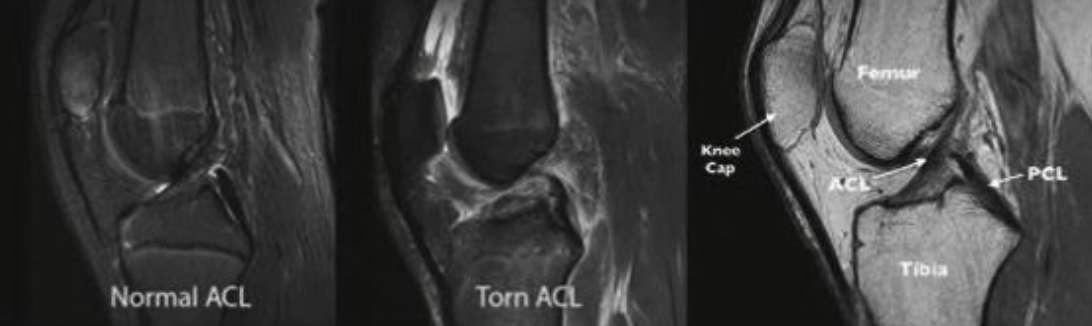
For mild ACL injuries or partial tears, healing ACL without surgery is possible through:
This approach works well for non-athletes or individuals with a sedentary lifestyle.
For complete ACL ruptures, surgery is often required, especially for active individuals or athletes.
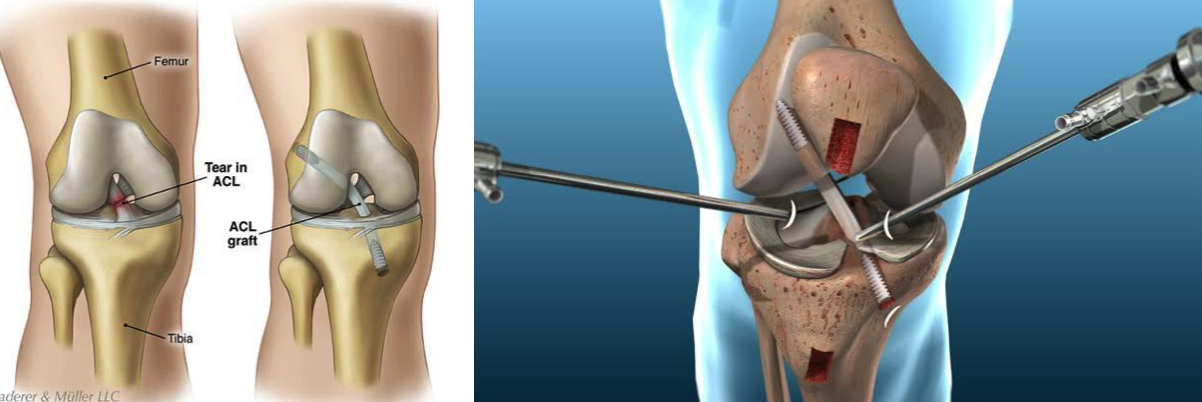
Post-surgical rehabilitation is crucial for regaining full knee function.
Recovery time varies depending on the severity of the injury and treatment method.
A structured physiotherapy program includes strengthening and mobility exercises. These exercises prevent stiffness and ensure the knee regains full function.
An ACL tear can significantly impact your life, but with proper treatment and rehab, full recovery is possible. Whether choosing physical therapy or ACL surgery, following a structured recovery plan is crucial for restoring knee function. If you’re dealing with an ACL injury, seeking timely care from an Orthopedic Doctor in Bangalore at a trusted Orthopedic Hospital in Bangalore can help you get back to daily activities and sports safely
A note from SPARSH Hospital Sports Injury Team Lead by Dr Vijay Kumar D
ACL tears are one of the most common knee injuries athletes experience. It can be extremely frustrating to miss months of practice, games or training sessions, but don’t rush your recovery. If you need surgery for Reconstruction of your ACL, you should be able to return to the field or court as soon as your knee has healed.
Don’t force yourself to use your knee if it’s hurt. Extra stress can make a lower grade ACL tear worse. Visit us as soon as you injure your knee or feel pain to get best treatment available at SPARSH Hospital, Bangalore.
An ACL tear hurts and can keep you from being active. The Orthopaedic Sports injury Team at SPARSH Hospital, led by Dr Vijay D, will provide you with world-class treatment, including reconstruction of your torn ACL and post-operative physiotherapy, and help you get back on your feet.
There might not be any way to prevent an ACL tear, especially if you’re an athlete. Sports injuries and accidents you can’t plan for usually cause ACL tears.
During sports or other physical activities:
Follow these general safety tips to reduce your risk of an injury:
A torn ACL can’t heal on its own, but it’s possible to live with it (especially if you have a low-grade tear). But if you’re an athlete/young adult or want to return to physical activity, you’ll need surgery to reconstruct your ACL. Most people choose to have an ACL tear surgically repaired.
Some people can walk with a torn ACL. But don’t force yourself to move or use your knee if it hurts. Visit an Orthopaedics Surgeon when you feel pain or have other knee injury symptoms. Putting more stress on your injured ACL can make a small tear worse.
Yes, an ACL tear affects knee stability and can lead to long-term complications if untreated. Severe cases require surgery for full recovery.
With rehabilitation, many people resume normal activities, but high-impact sports may be challenging without surgical repair.
For athletes and active individuals, it can be a significant setback, but with proper treatment, most people recover well and regain knee function.
It usually takes six to nine months to recover from a torn ACL after surgery and post-operative physiotherapy. Competitive athletes may need a little longer than this to heal fully before they’re cleared to return to their sport.
There’s a small chance you’ll tear the same ACL again in the future, even if you have surgery to repair it. Fewer than 10% of people who have a torn ACL tear that same ACL again. Talk to your surgeon about what to expect.
Most ACL tears aren’t career-ending. Just make sure you don’t rush your recovery. Most people who experience a torn ACL can return to their sport with no long-term consequences. Rehabilitation after your surgery is the best way to restore your knee’s strength and flexibility. You’ll need to rehab your knee over time before you can return to your sport.
Ask your treating orthopaedics surgeon if it’s safe for you to play the same sport again and when you can resume practice or training.
If you experience persistent knee pain, swelling, or instability, it is advisable to seek expert care. Visit an orthopaedic surgeon as soon as possible after you injure your knee. Talk to your doctor if you notice new symptoms or if the pain is getting worse.
You can consult some of the best orthopaedic doctors in Bangalore at SPARSH, which is renowned as one of the best orthopaedic hospitals in Bangalore, for specialised treatment.
Categories: Orthopedics
ACL Tear & Injury: Symptoms & Recovery is available for appointments. Please fill the below form to book an appointment.
Unlock the door to exceptional healthcare, book an appointment with SPARSH Hospital and let your journey to wellness begin.