A blood clot in the brain, also known as a cerebral thrombosis or stroke due to clotting, occurs when a clot obstructs blood flow to the brain. This can cause severe neurological symptoms like headaches, dizziness, paralysis, or speech difficulties. The condition can be life-threatening and requires immediate medical intervention. Treatment options include medications, surgery, and lifestyle changes to prevent recurrence.
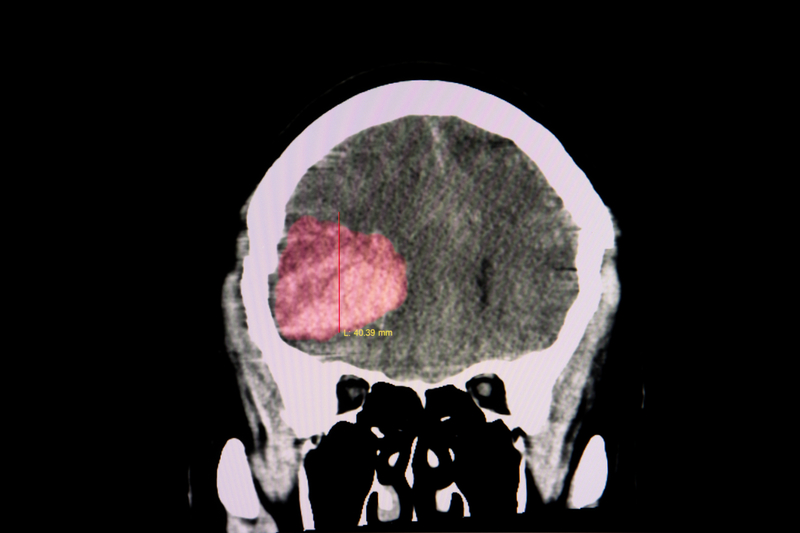
A blood clot in the brain occurs when a mass of coagulated blood forms inside the blood vessels supplying the brain. This can block oxygen and nutrients from reaching brain cells, leading to severe damage or even stroke. Blood clots in the brain typically result from arterial blockages (ischemic stroke) or venous clots (cerebral venous sinus thrombosis – CVST).
The severity of a blood clot depends on its size, location, and how quickly medical treatment is administered. If left untreated, it can lead to permanent brain damage or death. While brain clot treatment has improved over the years, early detection remains critical for survival and recovery.
Recognising the symptoms of a blood clot in the brain can be life-saving. These symptoms often develop suddenly and require urgent medical attention:
A thunderclap headache that appears out of nowhere could indicate a brain clot or stroke.
Numbness or loss of movement, typically on one side of the body, is a key warning sign.
Slurred or confused speech can signal a disruption in the brain’s function.
Blurry or double vision, or even temporary blindness, may occur.
Feeling unsteady or struggling to walk properly can indicate a neurological problem.
In some cases, blood clots in the brain may trigger seizures, especially if oxygen supply is severely compromised.
If you or someone you know experiences these symptoms that indicate a blood clot in the brain, seek emergency medical care immediately.
Several factors can contribute to the formation of blood clots in the brain. Some of the most common causes include:
Plaque buildup in the arteries narrows the blood vessels, increasing the risk of blood clots that can travel to the brain.
Uncontrolled hypertension puts pressure on blood vessels, making clot formation more likely.
Conditions like atrial fibrillation (irregular heartbeat) can cause blood to pool and form clots that may travel to the brain.
A traumatic brain injury can damage blood vessels, leading to clot formation in the brain.
Certain blood disorders, like thrombophilia, increase clotting tendencies, making brain clots more likely.
Lack of physical activity slows blood circulation, increasing the risk of clot formation.
Both habits contribute to poor vascular health and increase the risk of brain clots.
High blood sugar damages blood vessels over time, increasing clot formation risks.
Certain hormonal treatments can make blood thicker and more prone to clotting.
Understanding what causes blood clots can help in prevention and early detection.
The treatment for a blood clot in the brain depends on the severity and location of the clot. Some of the most effective brain clot treatment options include:
Early intervention can significantly improve the blood clot in brain survival rate. Seek immediate medical care if you experience:
If you are in Bangalore and have risk factors such as hypertension, diabetes, or previous strokes, consider visiting SPARSH, a neuroscience hospital in Bangalore. Here you can speak with some of the best neurologists in Bangalore who can provide the right treatment and preventive care.
A blood clot in the brain is a serious condition that requires urgent medical attention. Early detection and treatment are crucial in preventing long-term complications or fatalities. Understanding what causes blood clots, recognising symptoms, and seeking prompt brain clot treatment can save lives
Treatment depends on the severity of the clot. Mild cases are managed with blood thinners to prevent further clotting, while more serious cases may require clot-busting medications or even surgical removal (thrombectomy) to restore blood flow.
Recovery varies from person to person. Some regain full function, especially with early treatment, while others may have lingering effects like memory issues or muscle weakness. The key is early medical intervention and rehabilitation to improve outcomes.
For larger or life-threatening clots, thrombectomy is performed using a catheter to remove the clot. In severe cases, craniotomy (open-brain surgery) may be needed, especially if there’s swelling or internal bleeding.
With the right treatment, smaller clots can dissolve within a few days to weeks. However, some patients may need lifelong blood thinners to prevent future clots, especially if they have underlying health conditions like heart disease or high blood pressure.
Categories: Neurology
Blood Clot in the Brain: Symptoms, Causes & Treatment is available for appointments. Please fill the below form to book an appointment.
Unlock the door to exceptional healthcare, book an appointment with SPARSH Hospital and let your journey to wellness begin.