Arthritis is a common yet often misunderstood condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It refers to inflammation of the joints, which can lead to arthritis pain, swelling, and stiffness, significantly impacting one’s quality of life. This page serves as a comprehensive guide to understanding arthritis, its symptoms, causes, and treatment options.
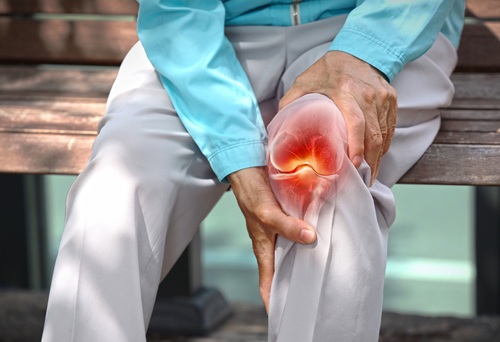
Arthritis is not a single disease, but a term used to describe a range of conditions that cause joint inflammation. It includes over 100 types, with osteoarthritis (OA) and rheumatoid arthritis (RA) being the most prevalent.
The symptoms of arthritis can vary depending on the type but commonly include:
The causes of arthritis vary based on the type, but they all result in joint inflammation and damage. Here's a detailed explanation of the main factors:
One of the most common arthritis causes is wear and tear on the joints. Over time, or with repetitive use, the cartilage that cushions the bones in a joint may gradually break down. This is the hallmark of osteoarthritis, often associated with aging, excessive physical activity, or joint injuries. As cartilage wears away, bones can rub together, leading to pain, swelling, and stiffness.
In some cases, the body's immune system mistakenly targets its own tissues, causing inflammation and joint damage. This is seen in rheumatoid arthritis, where the immune system attacks the synovium (the lining of the joints). This condition leads to chronic inflammation, deformity, and loss of joint function if left untreated.
Certain infections, such as bacterial or viral infections, can lead to arthritis. For example, viral arthritis occurs when a virus triggers joint inflammation. These types of arthritis are often temporary but may require targeted arthritis treatment to manage symptoms effectively.
Your genetic makeup can predispose you to arthritis, especially if there’s a family history of the condition. Additionally, lifestyle factors like obesity increase joint stress, especially in weight-bearing joints like the knees and hips, contributing to arthritis pain. Joint injuries, whether from sports or accidents, can also accelerate joint wear and tear, raising the likelihood of developing arthritis later in life.
Diagnosing arthritis requires a combination of medical history, physical exams, and tests:
Medical history and physical examination: Doctors assess arthritis pain, swelling, and mobility issues.
Imaging tests: X-rays, MRIs, or ultrasounds can help detect joint damage.
Blood tests: These identify inflammation markers or specific antibodies linked to autoimmune arthritis.
Joint fluid analysis: Testing fluid from the affected joint can rule out infections or gout.
Managing arthritis involves a combination of medical treatments, lifestyle changes, and self-care strategies:
Medications:
Arthritis Remedies
Severe cases might require surgical interventions, such as joint replacement, especially in advanced osteoarthritis.
Physical Therapy:
Therapists recommend exercises to improve strength, flexibility, and joint mobility, which can significantly contribute to arthritis pain relief.
Lifestyle Changes:
Seek medical attention if you experience:
Early intervention by an arthritis doctor is essential to slow disease progression and preserve joint function.
Arthritis can be challenging to live with, but timely diagnosis and proper management can greatly improve quality of life. Whether it's through medication, lifestyle changes, or physical therapy, there are numerous ways to find arthritis pain relief and regain mobility. If you are looking for rheumatologists in Bangalore, please visit your nearest SPARSH Hospital for expert treatment.
What is the main cause of arthritis?
The causes depend on the type of arthritis but can include wear and tear, autoimmune disorders, infections, and genetic predisposition.
What helps arthritis?
Treatments like medications, physical therapy, and lifestyle adjustments, such as exercise and weight management, can alleviate symptoms.
Why is arthritis so painful?
Joint pain arises from inflammation, cartilage wear, or damage to surrounding tissues, depending on the type of arthritis.
How to treat arthritis in the knee?
Treatment may include medications, physical therapy, knee braces, or in severe cases, surgical options like joint replacement.